Subtotal $0.00
Shopping cart
- Phone:+91 9892651388
- Email:dr.mud1710@gmail.com
- Mumbai
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body processes blood sugar (glucose). If left unmanaged, it can lead to serious complications like heart disease, kidney failure, and vision loss. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and preventive measures can help you take control of your health and avoid long-term complications.
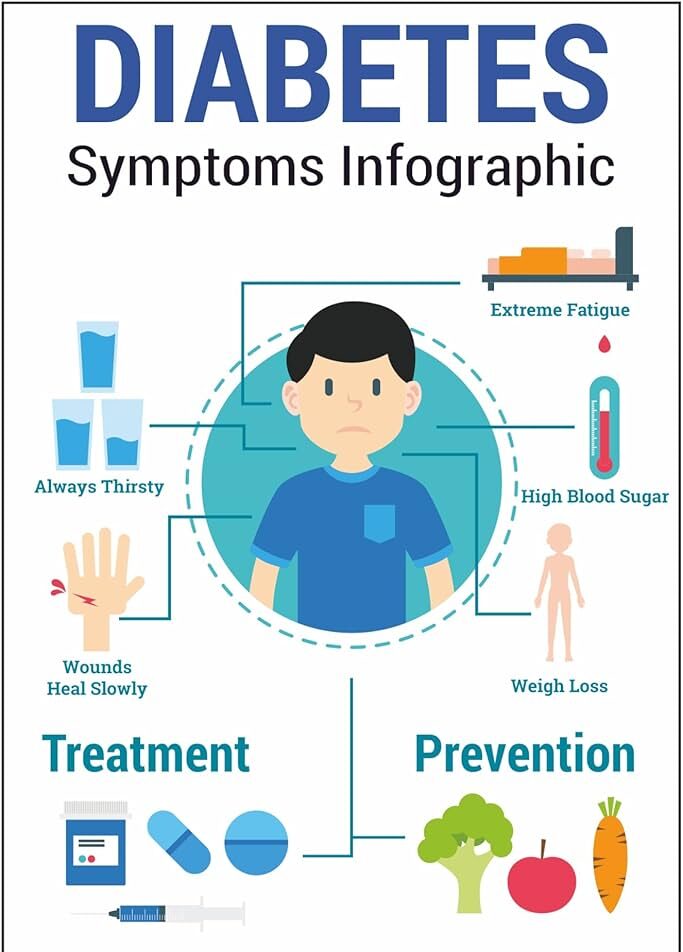
Diabetes occurs when the body cannot effectively use or produce insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels. There are three main types:
🔹 Type 1 Diabetes – The body does not produce insulin (autoimmune condition).
🔹 Type 2 Diabetes – The body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough.
🔹 Gestational Diabetes – Temporary diabetes that occurs during pregnancy.
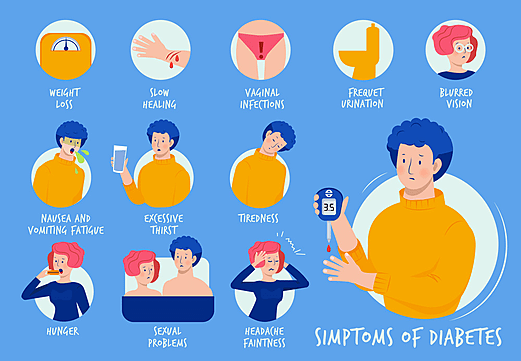
Early detection of diabetes can prevent complications. Watch for these warning signs:
🔹 Increased thirst and frequent urination
🔹 Unexplained weight loss or gain
🔹 Fatigue and constant tiredness
🔹 Blurred vision
🔹 Slow healing of wounds and infections
🔹 Tingling or numbness in hands and feet

Understanding what leads to diabetes can help in its prevention.
🧬 Genetics: Family history of diabetes increases the risk.
🍔 Unhealthy Diet: Excess sugar and processed foods can contribute.
🏋️ Lack of Physical Activity: Increases insulin resistance.
⚖️ Obesity: A major risk factor, especially for Type 2 diabetes.
⚕️ Other Medical Conditions: High blood pressure, PCOS, and cholesterol issues.



You can reduce the risk of diabetes with lifestyle modifications.
✔ Choose whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
✔ Avoid sugary drinks, junk food, and refined carbohydrates.
✔ Opt for lean proteins like fish, chicken, and legumes.
✔ Aim for 30 minutes of physical activity, 5 days a week.
✔ Engage in walking, swimming, cycling, or yoga.
✔ Strength training helps with insulin sensitivity.
✔ Even a 5-10% weight reduction helps prevent diabetes.
✔ Track calorie intake and focus on portion control.
✔ Check blood sugar levels regularly if at risk.
✔ Consult a doctor if glucose levels fluctuate.
✔ Chronic stress affects insulin levels, so practice meditation or deep breathing.
✔ Aim for at least 7-9 hours of sleep per night
If you experience frequent thirst, excessive fatigue, or unexplained weight loss, consult a doctor immediately. Early diagnosis can prevent complications like:
🔹 Heart disease
🔹 Kidney failure
🔹 Nerve damage
🔹 Vision problems
Diabetes is a manageable condition with the right approach. By making small, consistent changes in diet, exercise, and lifestyle, you can prevent or control diabetes effectively.
💙 “Your health is in your hands – take control today for a healthier tomorrow!”